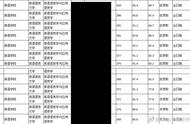
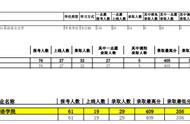
复习策略
词汇部分可用的参考书包括但不限于专四、专八、刘毅5000、刘毅10000、刘毅22000、GRE3000考法精析,此外在平时外刊精读和平时的阅读过程中出现的生词也要记住。
单词的记忆可以借助纸质书 APP,背诵就是先用纸质版认真学习每一个单词(可以查字典补充单词的例句/用法),一本纸质书完成两轮复习后可以用app每天过一部分已经背完的纸质书上的单词,然后开始背新的一本单词。单词的记忆要注意的是一定要反反复复的背诵,每天都要花半个小时到一个小时在单词上,以免遗忘。
常识部分一般是英美文学和语言学的选择题。该部分的题目非常有特点,语言学的选择题比较基础,但涉及的面比较广(戴的那本书有时间的可以简单过一下,只考选择题,理解即可),会考4题左右;文学的选择题一般来说比较偏,不是文学书或者参考书上涉及的,而且考的很少,一般1-2题左右,可以不用花太多时间在这一部分。
习题举例及知识点拓展总结
习题举例一:
The study of is syntax.
A.Textual organization
B.Sentence structure
C.Word formation
D.Language functions
这道题的答案是B,句法学(syntax)是对句子结构的研究。该题的知识点考察对语言学的分支的理解,这个知识点也是在考题中反复出现的,需要考生掌握不同分支的专业名称及其含义。以下是常考的几个分支学科的名词及其内涵:
Phonetics(the study of sounds);
Phonology(the study of sound patterns);
Morphology(rules about words);
Syntax(rules of sentences)
Semantics(the study of meaning in isolation)
Pragmatics(the study of meaning in context)
习题举例二:
The sentence A rose by any other name would smell as sweet reflect the feature of language
A.Arbitrariness
B.Productivity
C.Duality
D.Displacement
这道题的答案是A,这句话体现了语言的任意性(Arbitrariness)。任意性指的是语言符号和语言含义之间没有逻辑联系,是任意的。该知识点考察对语言识别特征的理解,这个知识点是高频考点,考试使用的句子也是书中的原句,需要考生掌握不同特征的专业名称及其含义。以下是常考的几个特征的名词及其内涵:
Arbitrariness:There is no logical connection between linguistic symbols and their meaning
Displacement: We can talk about things not related to the immediate situation
Cultural transmission: Our knowledge about language is not genetically transmitted, but culturally transmitted.
Productivity/Creativity: We can produce sentences we have never heard before.
习题举例三:
In the sentence He learned French two years ago, the underlined -ed is a
A.Free morpheme
B.Derivational morpheme
C.Inflectional morpheme
D.Root
这道题的答案是C,-ed是曲折词素(Inflectional morpheme)。曲折词素是指表征单复数、时态、所有格的词素。该知识点考察对不同词素的理解,需要考生准确判断不同词素。以下是常考的几个词素及其内涵:
Free morpheme: 这类词素可以单独成词
Derivational morpheme: 可以生成新的词汇的词素叫做派生词素
Inflectional morpheme:曲折词素是指表征单复数、时态、所有格的词素
习题举例四:
is the act of uttering words, phrases, and sentences.
A.Locutionary act
B.illocutionary act
C.Perlocutionary act
D.Primary speech act
这道题的答案是A,locutionary act 指的是言内行为。言内行为指的是借助词汇,句法等知识表达字面意思。该知识点考察对不同话语行为的理解,需要考生准确判断不同话语行为的区别。以下是常考的几个话语行为及其内涵:
Locutionary act:the act of conveying literal meaning by means of syntax, lexicon and phonology
Illocutionary act: the act of expressing the speaker’s intention
Perlocutionary act: the consequence or the change brought about by saying something
习题举例五:
Patient and doctor are a pair of antonyms.
A.Gradable
B.Complementary
C.Relational
D.Absolute
这道题的答案是C,医生和病人属于关系类反义词(relational antonym)。该类反义词是指两个词之间存在相反关系。该知识点考察对词义关系的理解,需要考生准确判断不同词义关系的区别。以下是三类反义词的内涵和例子:
Gradable antonym:两个词之间还有一个中间过程,如果是形容词一般都有比较级,如hot和cold
Complementary antonym:两个词中间没有中间过程,非此即彼,如alive 和dead
Relational antonym:两个词之间有相对关系,比如丈夫和妻子
高译教育专注上外及全国院校外语专业考研、保研辅导,专门致力于上海外国语大学考研、夏令营推免咨询辅导和全国其他院校外语专业考研、夏令营推免咨询辅导的教育服务机构。现阶段,针对上外各专业考研辅导暑期集训课程报名中,感兴趣的同学可以详细咨询高译考研辅导老师。